There are many greenhouse gases but these are some of the most important water vapour, H 2 O;Greenhouse gas Chemical formula Global Warming Potential, 100year time horizon Atmospheric Lifetime (years) Global Warming Potential and Atmospheric Lifetime for Major Greenhouse Gases;Since the Industrial Revolution, rising emissions of greenhouse gases—including carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and others—have been the driving force behind climate change Who is responsible for emitting the most greenhouse gases?

France Greenhouse Gas Emissions Decreased By 16 9 From 1990 Levels Climate Scorecard
Greenhouse games maine
Greenhouse games maine-Greenhouse gas emissions are greenhouse gases vented to the Earth's atmosphere because of humans the greenhouse effect of their 50 billion tons a year causes climate change Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels coal, oil, and natural gas15 hours ago Net zero announcement UK sets out plans to cut greenhouse gas emissions Another big push towards electric vehicles is being made in the UK government's latest strategy to make the great shift to




The Greenhouse Effect Climate Matters
9 hours ago UK sets out plans to cut greenhouse gas emissions More money for electric cars, onstreet charging points and planting trees have been announced as part of UK government efforts to drive down The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphere Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), ozone (O3), and fluorinated gasesMethane is the next of the greenhouse gases which has the biggest effect on global warming (15%) This is generated by activities such as livestock production, agriculture, sewage treatment, natural gas and oil distribution , coal mining, fuel use and is also given off from waste tips It lasts an average of 12 years in the atmosphere
Greenhouse gases warm the planet Scientists know with virtual certainty that increasing greenhouse gas concentrations tend to warm the planet In computerbased models, rising concentrations of greenhouse gases produce an increase in the average surface temperature of the earth over time The AGGI—short for Annual Greenhouse Gas Index—reports the combined warming influence of all longlived greenhouse gases as a fraction of their influence in 1990 Ever since people began grappling with the realization that human activities are changing the climate, scientists and decisionmakers have struggled to come up with simple ways to talk about the The most significant greenhouse gases, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), are water vapor (H2O), carbon dioxide
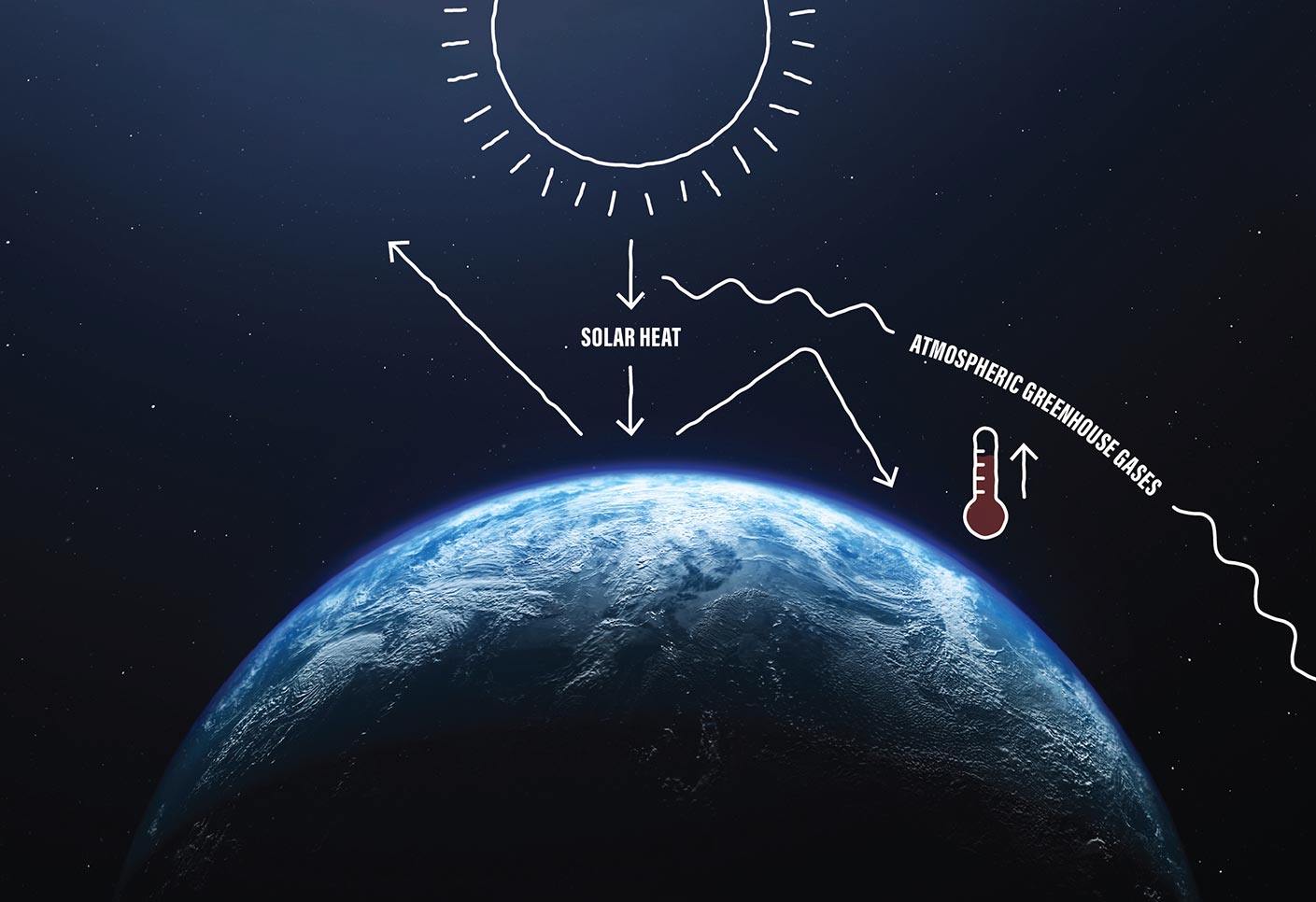
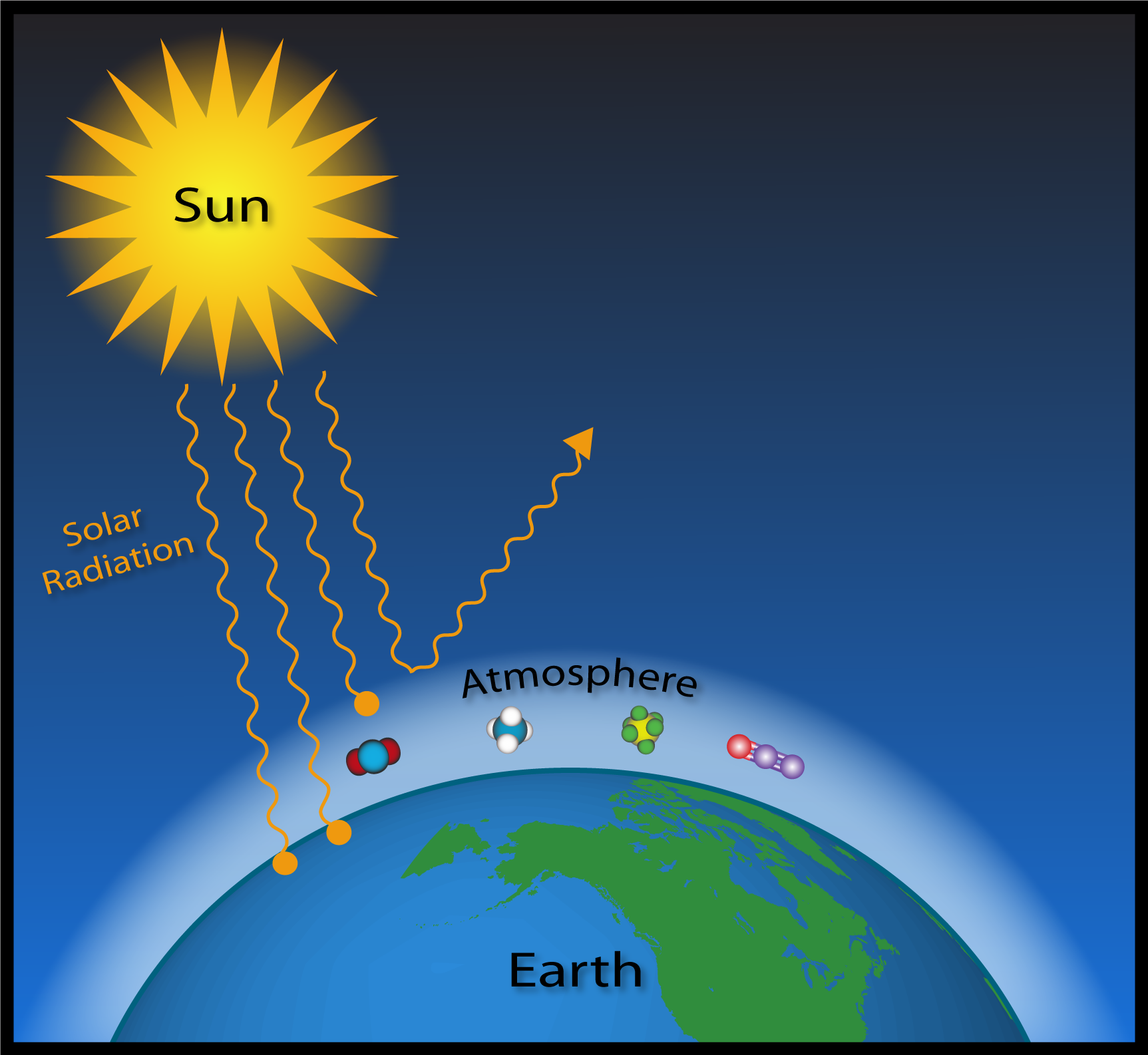
Greenhouse gases affect Earth's energy balance and climate The Sun serves as the primary energy source for Earth's climate Some of the incoming sunlight is reflected directly back into space, especially by bright surfaces such as ice and clouds, and the rest is absorbed by the surface and the atmosphereWhen we talk about greenhouse gases, we're referring to carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons and sulphur hexafluoride Greenhouse Gases Methane, Carbon Dioxide Share of Global GHG Emissions 3% A man scavenges for waste to recycle at a garbage dump in Linfen, China Landfill sites like this produce greenhouse gases because rotting organic waste like food waste emits methane which warms the atmosphere unless it is captured



Nasa At Your Table Where Food Meets Methane And The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gases The Australian Museum
Of the greenhouse gases, carbon dioxide (CO 2) is the most prominent Sources of atmospheric CO 2 include volcanoes, the combustion and decay of organic matter, respiration by aerobic (oxygenusing) organisms, and the burning of fossil fuels, clearing of land, and production of cement by humans These sources are balanced, on average, by a setCarbon dioxide (CO 2) is the most important greenhouse gas, but not the only one – gases such as methane and nitrous oxide are also a driver of global warming Carbon dioxideequivalents (CO 2 eq The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect include water vapor,
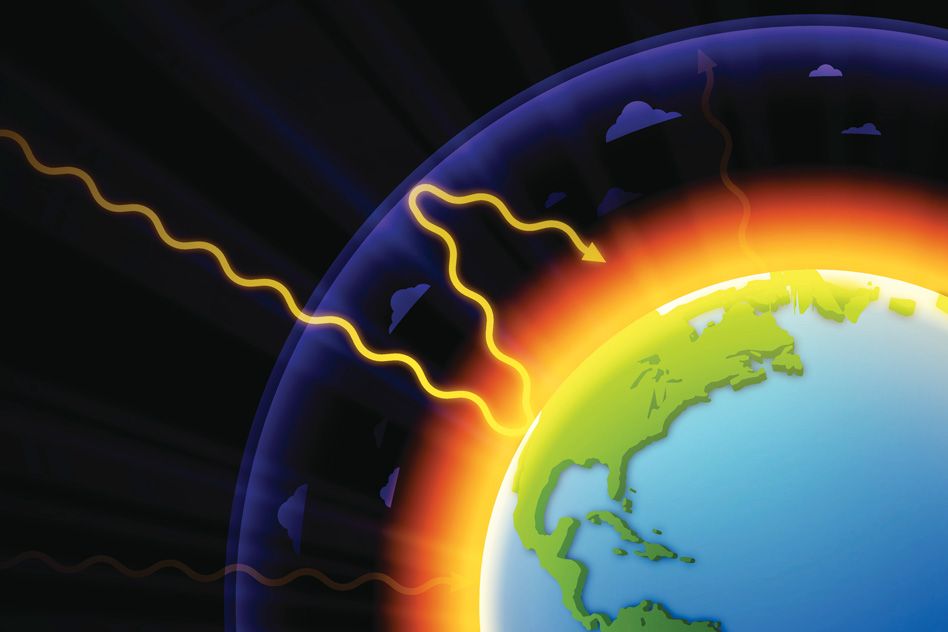




Explained Greenhouse Gases Mit News Massachusetts Institute Of Technology




Dark Greenhouse Gases Pie Chart Template
Carbon Dioxide CO2 1 100* Methane CH4 25 12 Nitrous Oxide N2O 265 121 Chlorofluorocarbon12 (CFC12) CCl2F2 10,0 100 Hydrofluorocarbon23 (HFC23) CHF3The term "greenhouse gases," or GHGs, covers a wide variety of gases that, once they are released into the atmosphere, trap the sun's heat When the sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and trapped in the lower atmosphere, heating the EarthGreenhouse gases are gases in an atmosphere that absorb and emit radiation within the thermal infrared range This process is the fundamental cause




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Carbon Streaming Corporation Greenhouse Gases
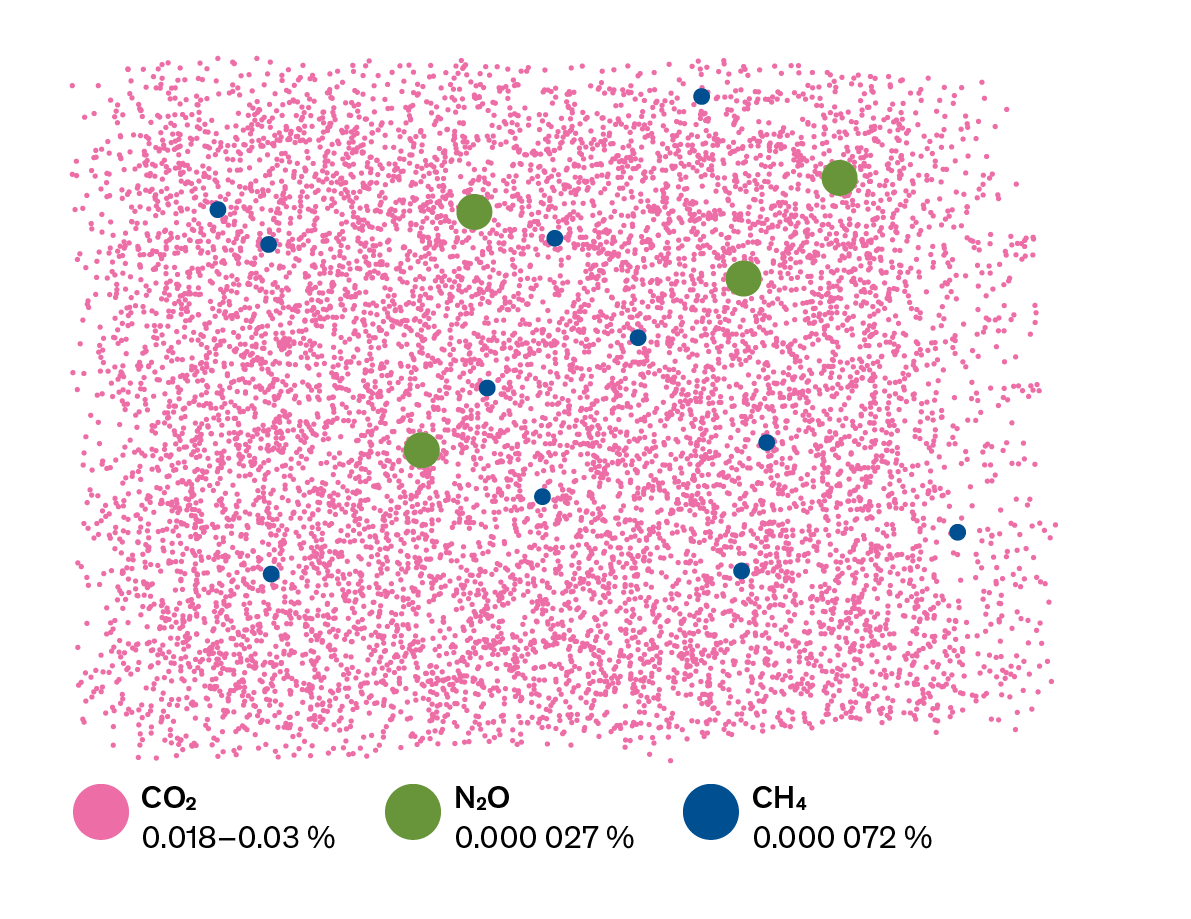
Carbon dioxide, CO 2;Scientists attribute the global warming trend observed since the mid th century to the human expansion of the "greenhouse effect" 1 — warming that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere block heat from escaping Longlived gases that remain semipermanently in the atmosphere and do not respond Major greenhouse gases and sources Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) Carbon dioxide is the primary greenhouse gas, responsible for about threequarters of emissions It can linger in the atmosphere for



3




Where Do Canada S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From
The Greenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon that insulates the Earth from the cold of space As incoming solar radiation is absorbed and reemitted back from the Earth's surface as infrared energy, greenhouse gases (GHGs) in the atmosphere prevent some of this heat from escaping into space, instead reflecting the energy back to further warm the surfaceGreenhouse gases that occur both naturally and from human activities include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and ozone (O 3) Other greenhouse gases have essentially no natural sources, but are side products of industrial processes or manufactured for human purposes such as cleaning agents, refrigerants, and electrical insulatorsAlthough greenhouse gases make up only about 1 percent of the Earth's atmosphere, they regulate our climate by trapping heat and holding it in a kind of warmair blanket that surrounds the planet




How Trump Is Ensuring That Greenhouse Gas Emissions Will Rise The New York Times




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey
Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), ozone (O3), and fluorinated gases View leveled Article Carbon Dioxide Levels Are at a Record High;8 hours ago Although it is a shortlived gas compared to carbon dioxide, which persists in the atmosphere for thousands of years, methane has a far more powerful greenhouse effect more than 32 times that of CO2What are "greenhouse gases?" The transparent windows of a greenhouse (or a car parked in the sunlight) transmit the warming visible rays of the sun, prevent the resulting warm air from leaving, and hence maintain a warmer environment inside than outside the structure In the Earth's atmosphere, some trace gases absorb infrared radiation




Countries Who Contribute The Least Greenhouse Gasses Worldatlas




What S The Deal With Greenhouse Gases Emissions And The Environment Futurelearn
Carbon dioxide (CO 2) makes up the vast majority of greenhouse gas emissions from the sector, but smaller amounts of methane (CH 4) and nitrous oxide (N 2 O) are also emitted These gases are released during the combustion of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, to produce electricityHere's What You Need To KnowGreenhouse gas definition is any of various gaseous compounds (such as carbon dioxide or methane) that absorb infrared radiation, trap heat in the atmosphere, and contribute to the greenhouse effect How to use greenhouse gas in a sentence




The Greenhouse Effect Cool Australia




Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society
Fluorinated Gases (HFCs, PFCs, SF 6) Fluorinated gases are emitted in smaller quantities than the other greenhouse gases, but what they lack in volume they can make up in potency and long lifespans in the atmosphere, ranging from 1270 years for HFCs to ,000 years for PFCs and about 3,0 years for SF6Greenhouse gases absorb reflected solar energy, making the Earth's atmosphere warmer A lot of the sun's energy reaches the ground directly, and a portion is reflected by the ground back intoLand use, landuse change, and forestry (LULUCF), also referred to as forestry and other land use (FOLU), is defined by the United Nations Climate Change Secretariat as a "greenhouse gas inventory sector that covers emissions and removals of greenhouse gases resulting from direct humaninduced land use such as settlements and commercial uses, landuse change, and




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
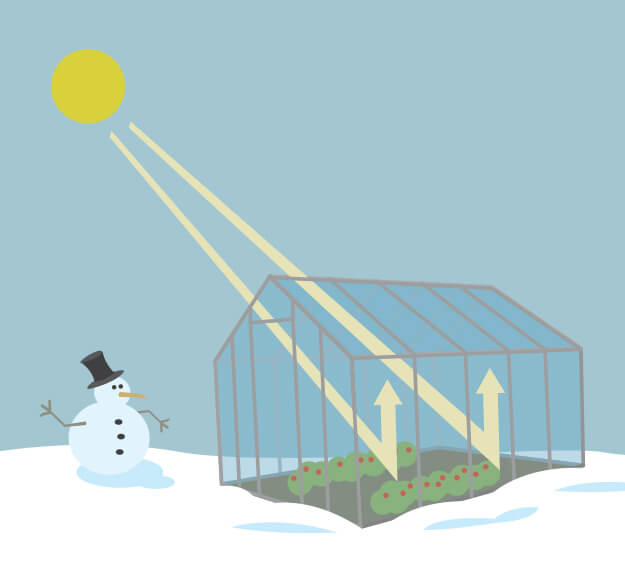




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids
Greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and waterGreenhouse gas definition, any of the gases whose absorption of solar radiation is responsible for the greenhouse effect, including carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, andGreenhouse gas definition 1 a gas that causes the greenhouse effect, especially carbon dioxide 2 a gas that causes the Learn more




France Greenhouse Gas Emissions Decreased By 16 9 From 1990 Levels Climate Scorecard




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
The answer may not be as clear as one might assume, because the top emitters change depending on how the data is collected and whatGreenhouse gases are gases—like carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane, and nitrous oxide—that keep the Earth warmer than it would be without themThe reason they warm the Earth has to do with the way energy enters and leaves our atmosphereWhen energy from the Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides Scientists have determined that carbon dioxide's warming effect helps stabilize Earth's atmosphere Remove carbon dioxide, and the terrestrial greenhouse effect would collapse Without carbon dioxide, Earth's surface would be some 33 °C (59 °F) cooler



The Greenhouse Effect




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia



Greenhouse Gasses Captain John Smith Chesapeake National Historic Trail U S National Park Service



What Are Greenhouse Gases Myclimate




The Greenhouse Effect Climate Matters



3



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere Is At A Record High Here S What You Need To Know
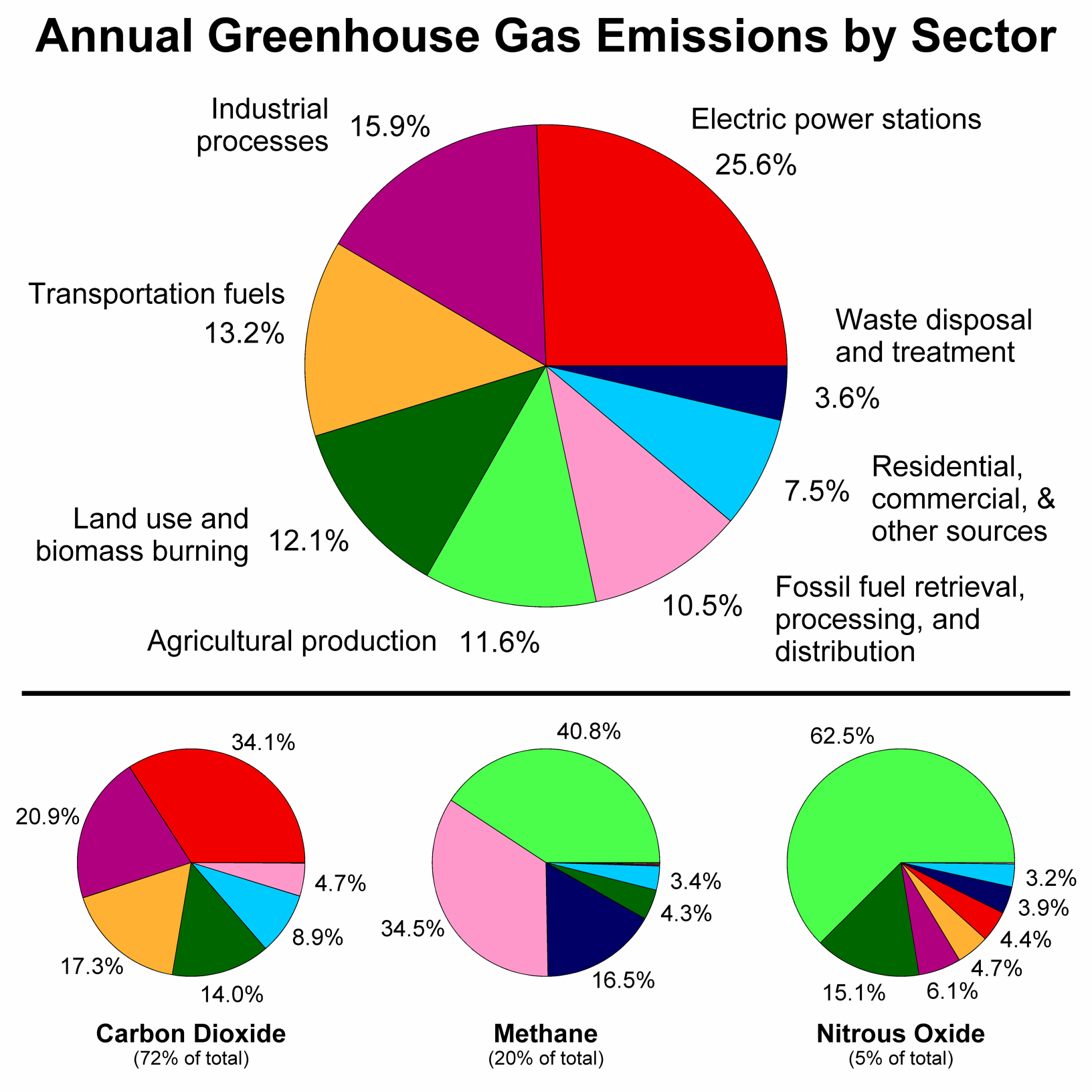



File Greenhouse Gas By Sector Png Wikimedia Commons



1




What Would Happen To The Climate If We Stopped Emitting Greenhouse Gases Today




Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gases Youtube



Global Warming Greenhouse Gas Models For Kids




What Are Greenhouse Gases David Suzuki Foundation




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Greenhouse Effect Video For Kids The Greenhouse Effect Youtube




Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa




Greenhouse Gases 101 Ben Jerry S




Noaa Index Tracks How Greenhouse Gas Pollution Amplified Global Warming In Welcome To Noaa Research




Human Influence On The Greenhouse Effect Globalchange Gov




Greenhouse Effect What Is It Definition And Role In Global Warming



How Greenhouse Gases Influence Climate The Weather Gamut




Greenhouse Gases What Is Warming Up Our Earth
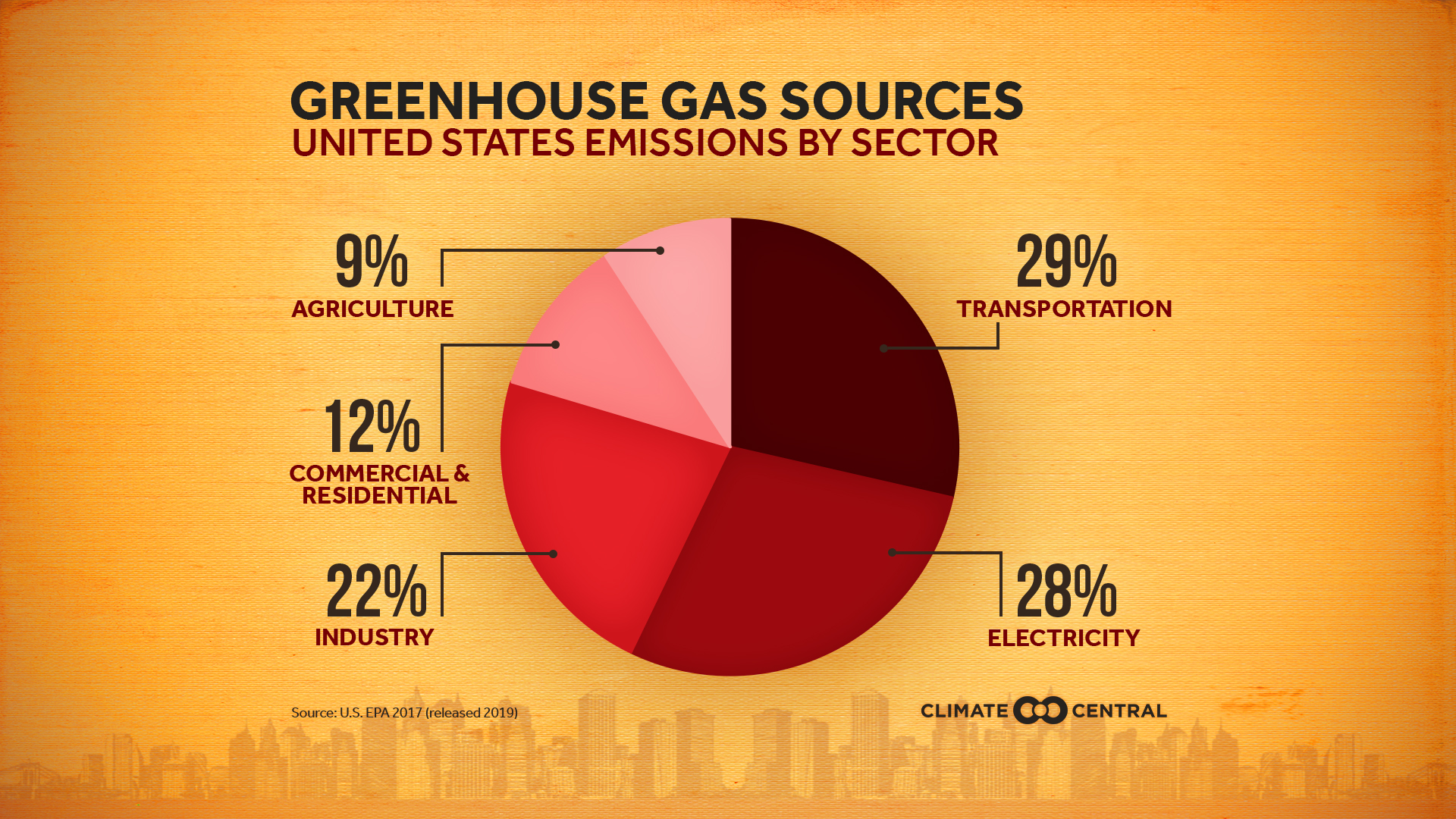



Emissions Sources Climate Central




The Greenhouse Gases Airclim




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
.png)



Greenhouse Effect Energy Education
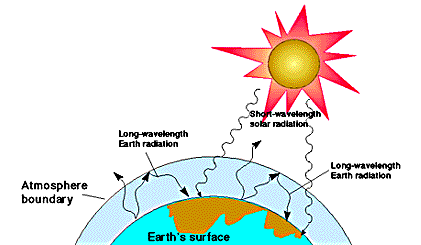



Greenhouse Effect Its Causes And Effect List Of Greenhouse Gases




Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
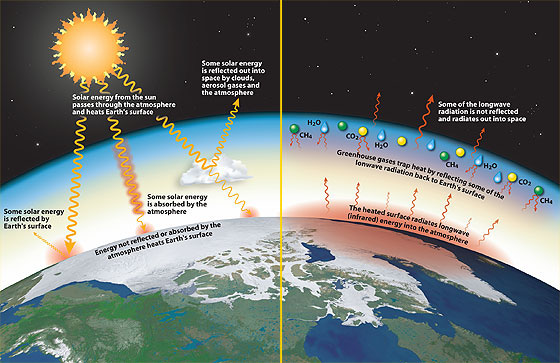



Too Much Of A Good Thing




Noaa S Greenhouse Gas Index Up 41 Percent Since 1990 Welcome To Noaa Research




The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
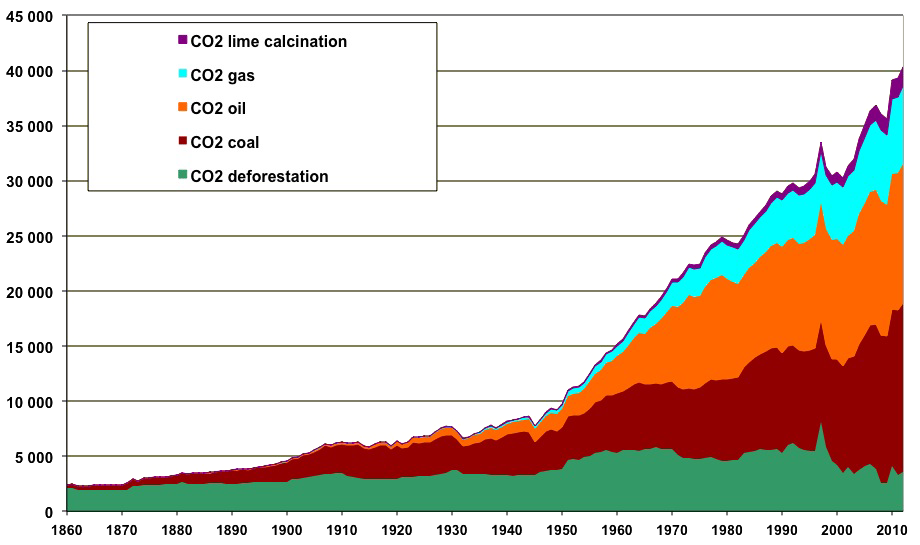



How Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Presently Evolve Jean Marc Jancovici
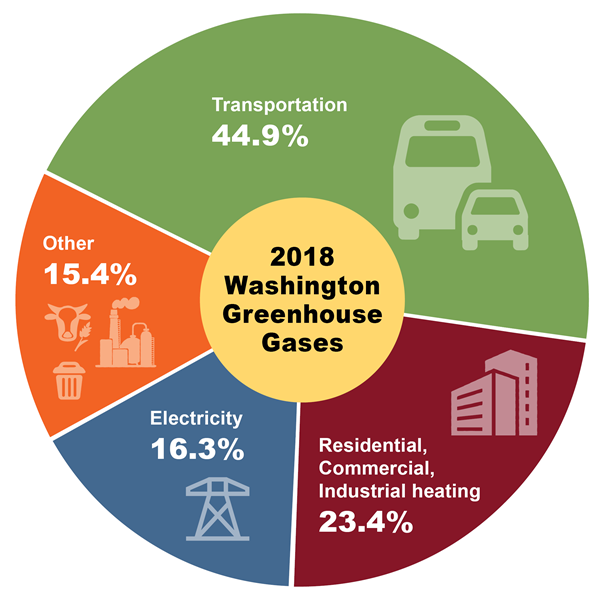



18 Data Washington State Department Of Ecology




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Space




Air Pollution Greenhouse Gases Britannica




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa
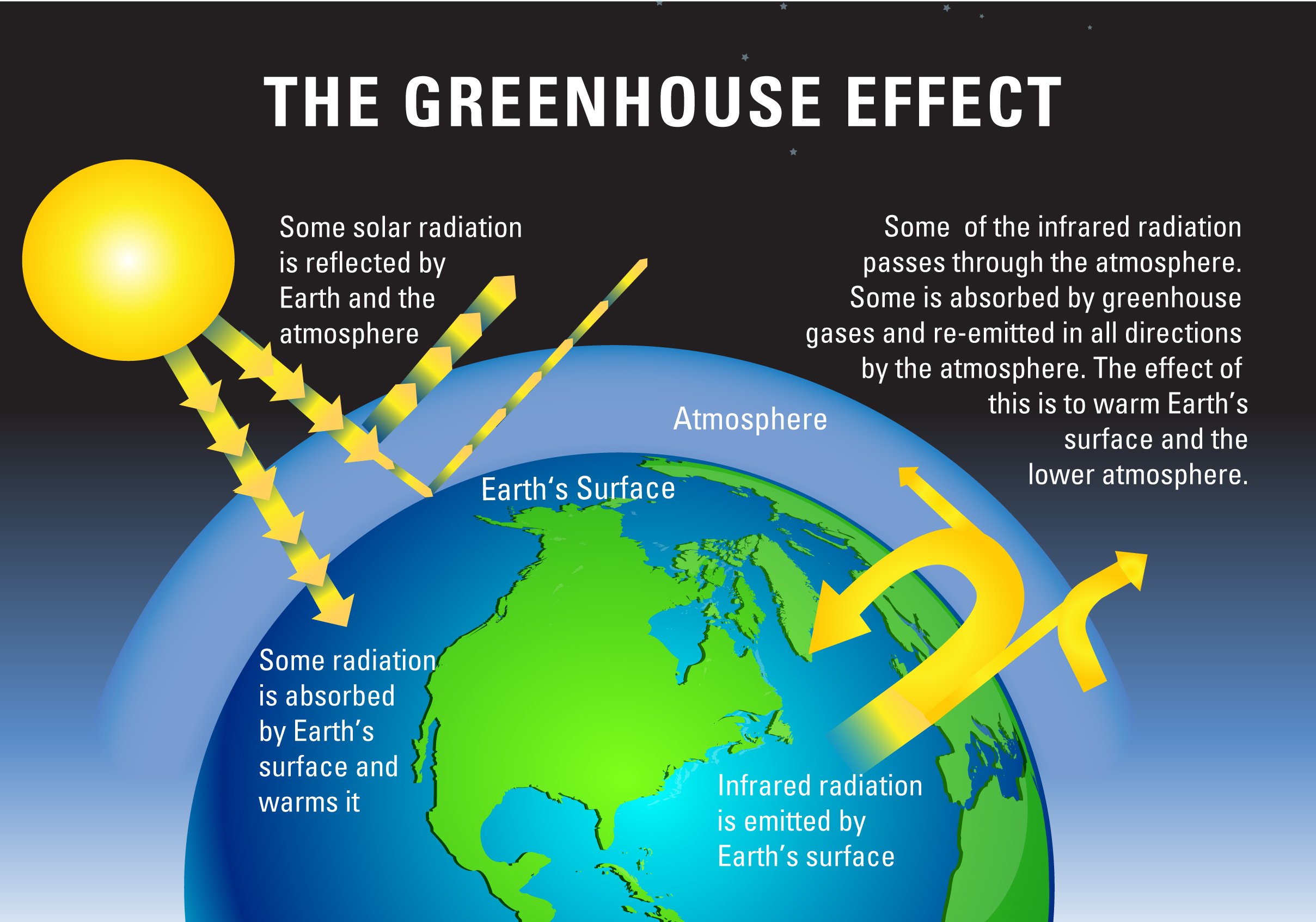



Greenhouse Gases Earth Journalism Network




Greenhouse Gases Bioninja



Greenhouse Gases




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




The Greenhouse Effect Artis Energy



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate



1




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students
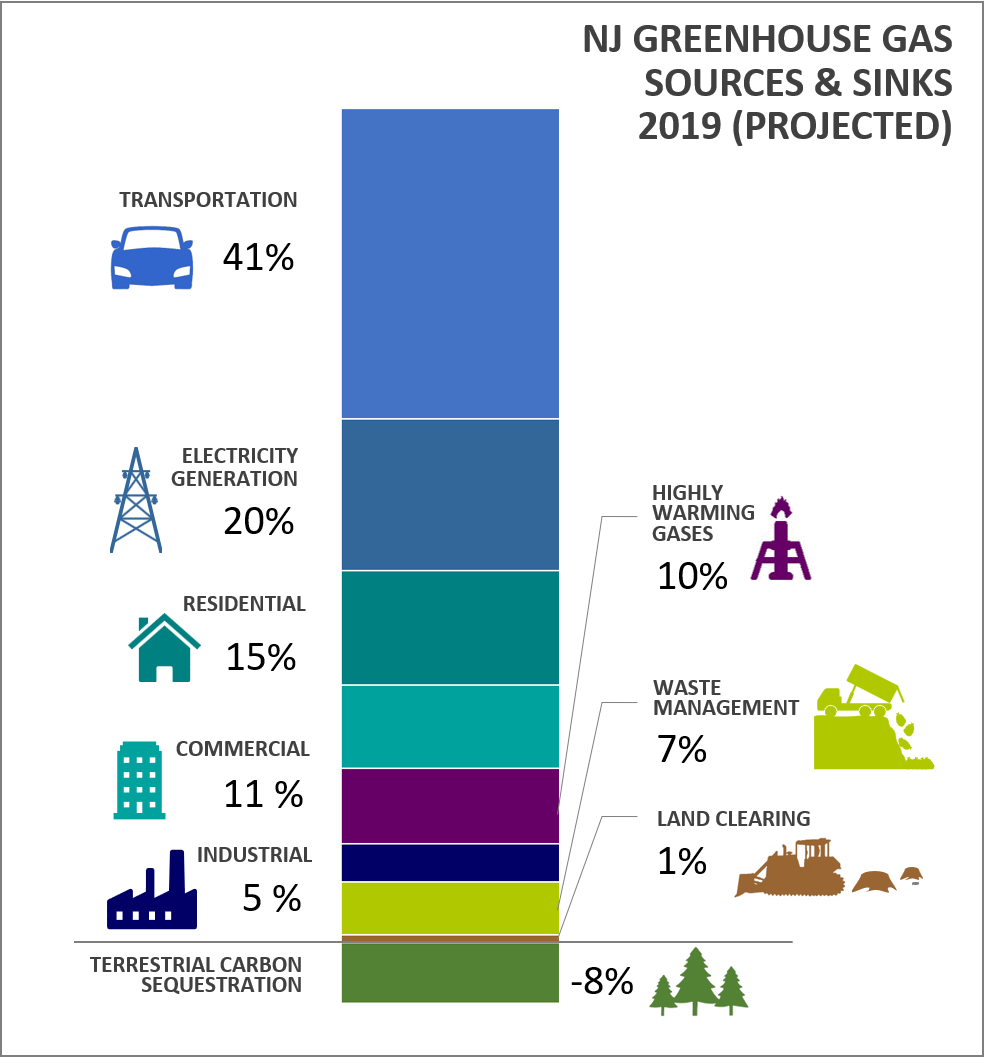



Njdep Air Quality Energy Sustainability
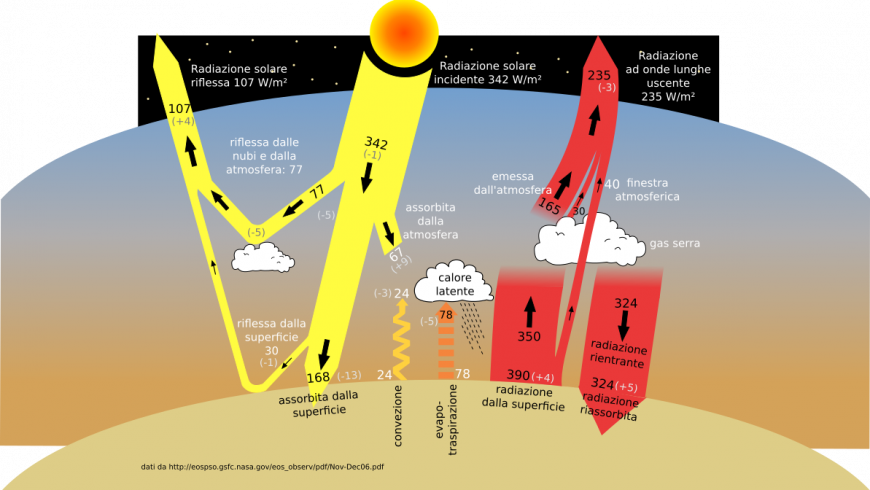



Greenhouse Gases What Are They What Can We Do To Reduce Emissions




Greenhouse Effect Stock Illustrations 3 213 Greenhouse Effect Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




Usgcrp Indicator Details Globalchange Gov
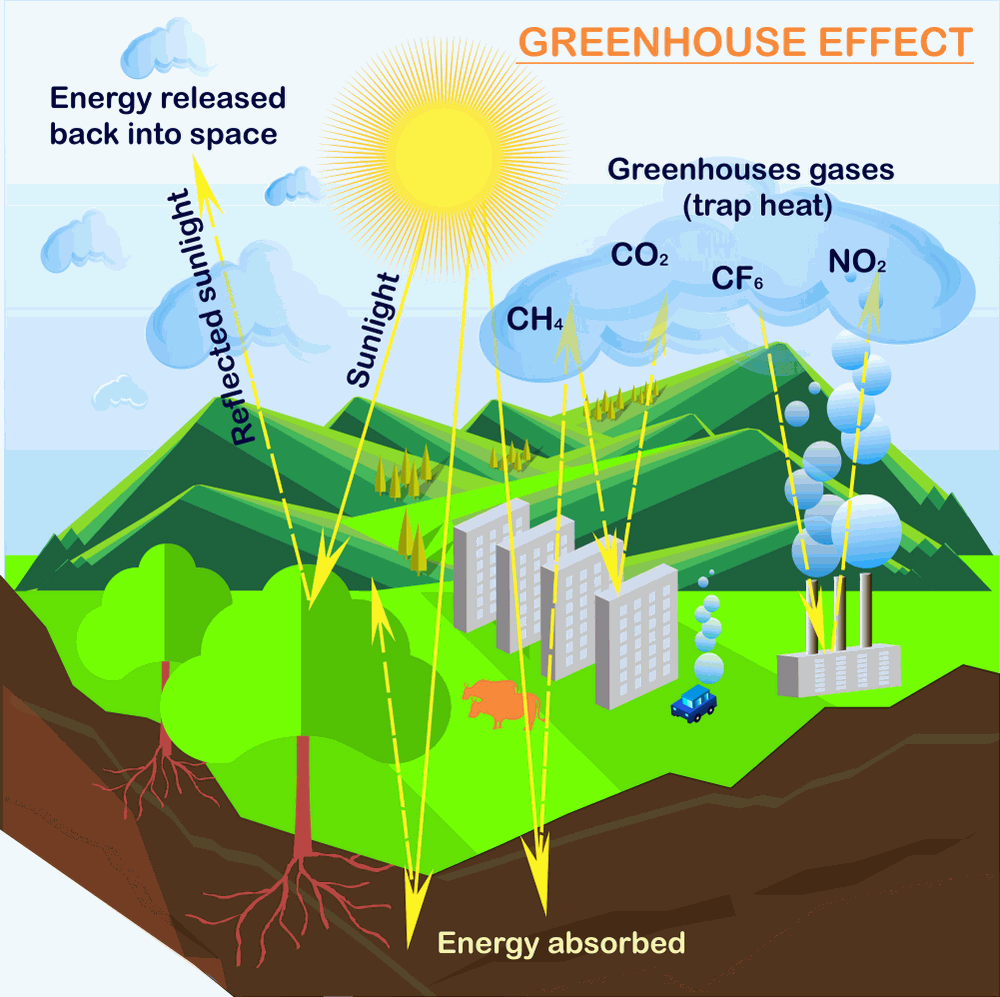



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Global Warming 19




Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet




Greenhouse Gases Causes Sources And Environmental Effects Live Science




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Weatherquestions Com What Is The Greenhouse Effect What Are Greenhouse Gases



The Greenhouse Effect




The Greenhouse Effect World101




What Are Greenhouse Gases Saving Earth Encyclopedia Britannica




Cutting Greenhouse Gases From Food Production Is Urgent Scientists Say The New York Times
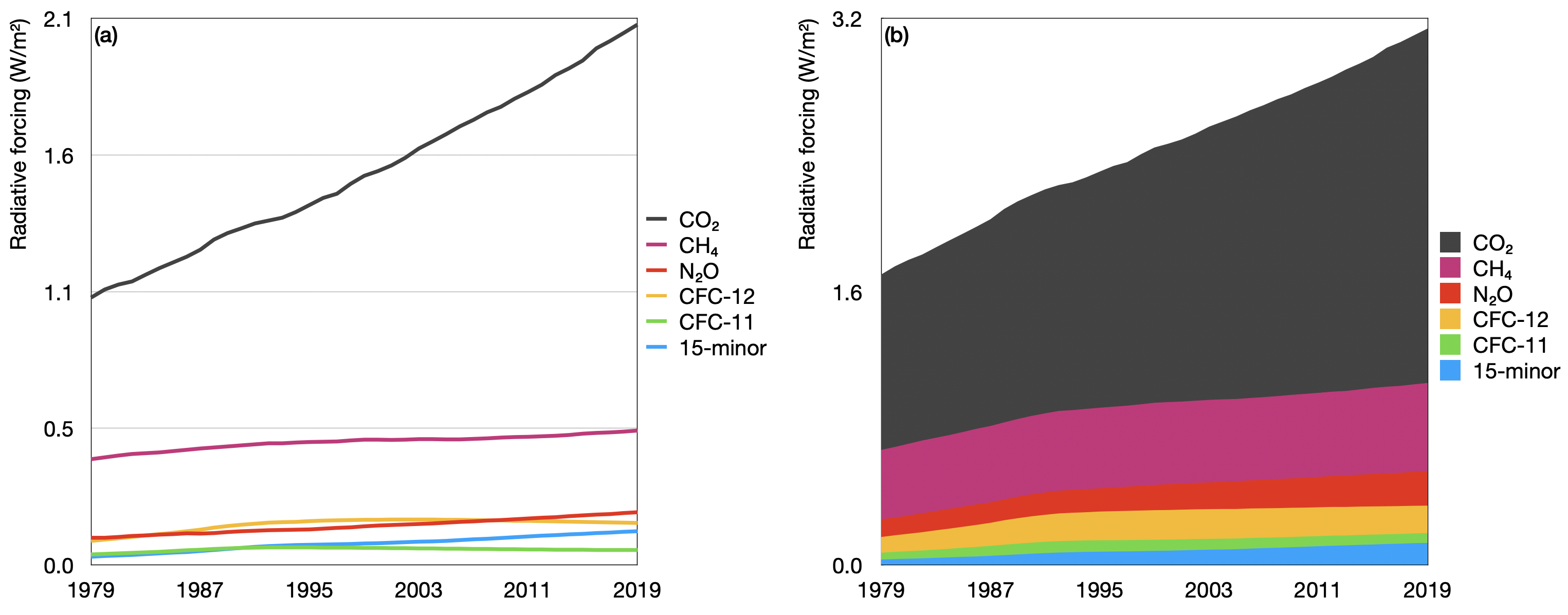



Greenhouse Gas Emissions World Energy Data




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Caltech Science Exchange




Why Providing Alternatives To Sf6 And Other Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus
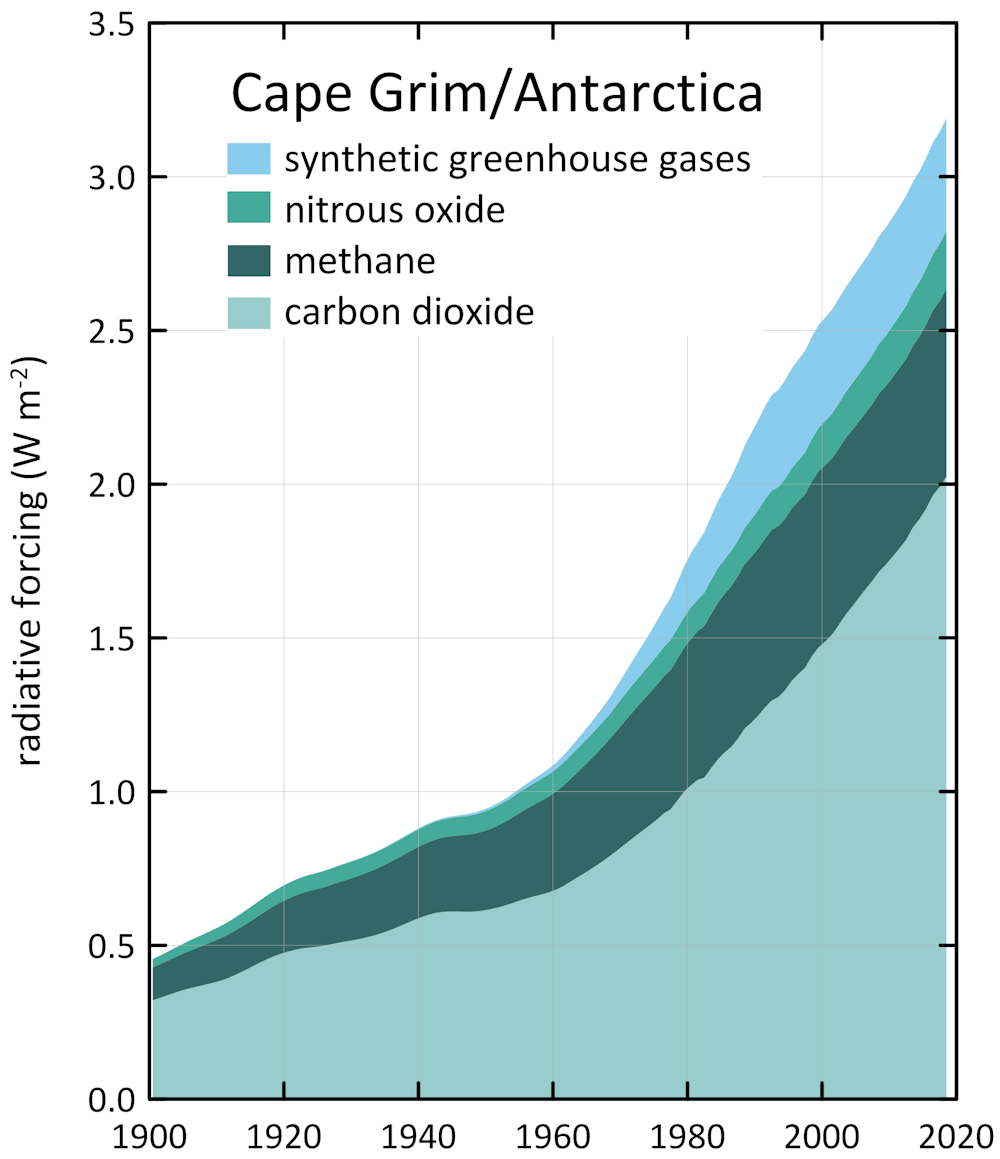



Why There S More Greenhouse Gas In The Atmosphere Than You May Have Realised




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
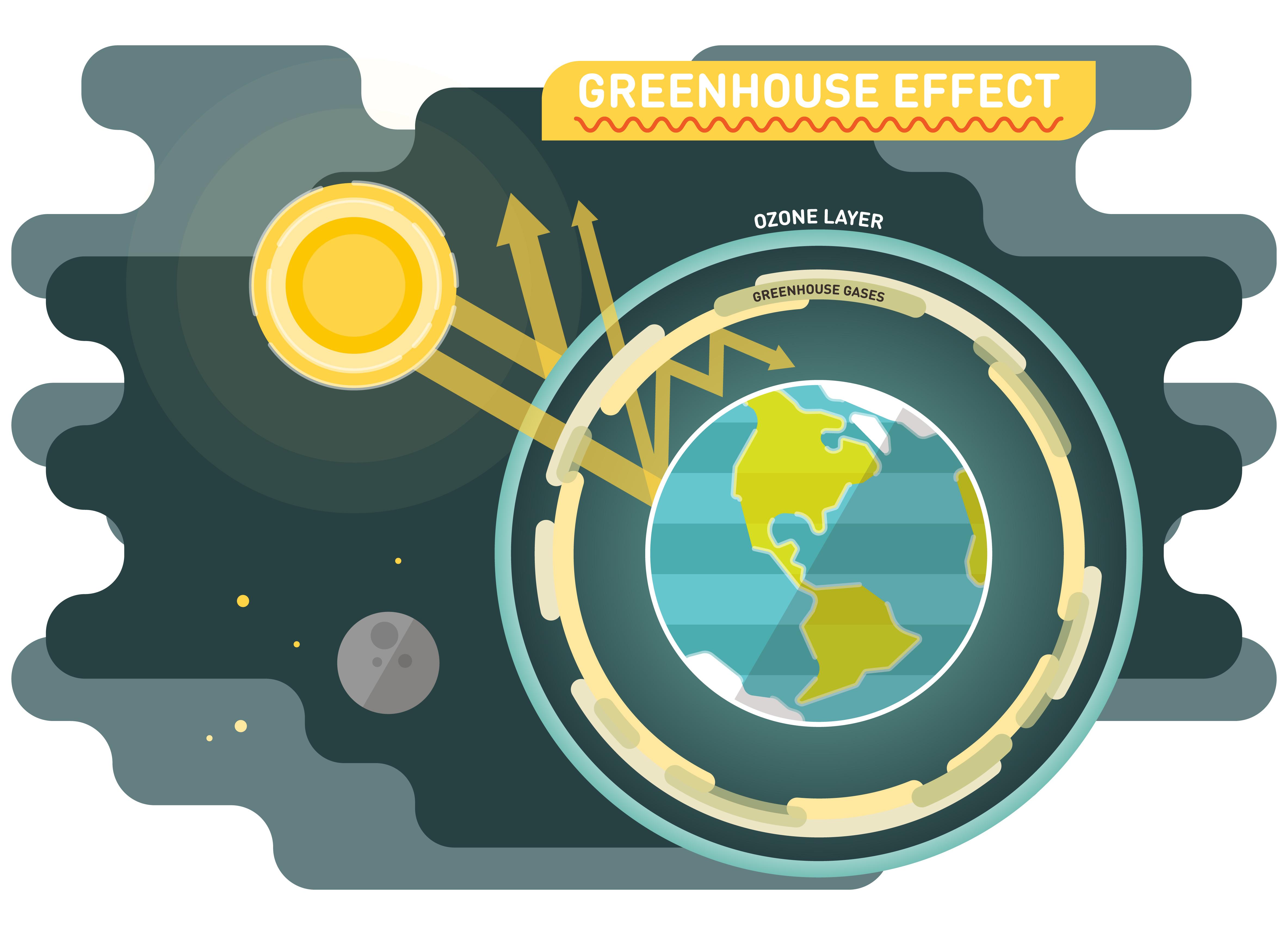



Why The Greenhouse Effect Is Important How It Affects The Climate




Human Activity Caused The Long Term Growth Of Greenhouse Gas Methane




Greenhouse Gas Pollution All About Ghg S And What To Do About Them
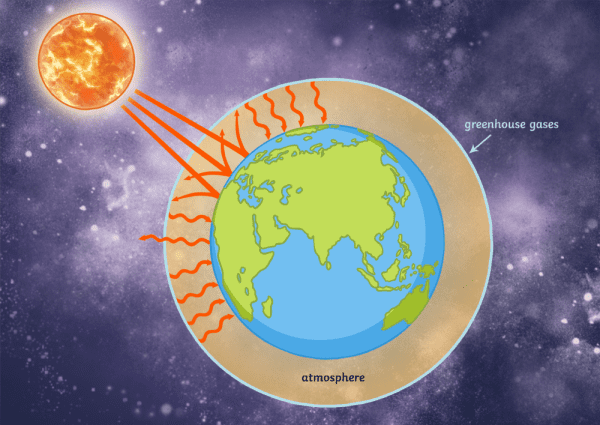



What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki




Greenhouse Gases 101 Ben Jerry S




Indicator Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Indicator Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Gcis
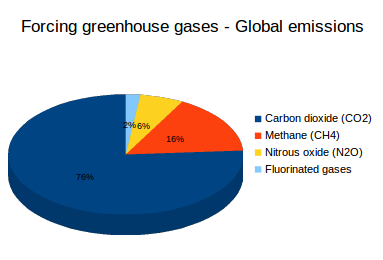



What Are Greenhouse Gases What S Your Impact




Greenhouse Gases World Meteorological Organization
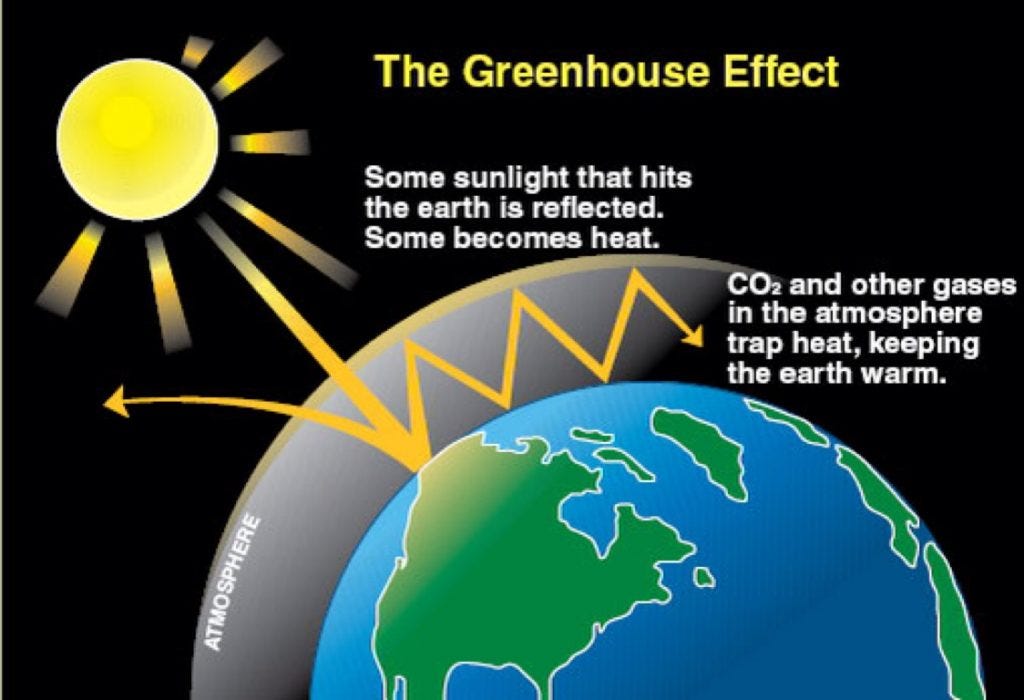



Greenhouse Effect Advantages And Disadvantages By Tutorbin Medium




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia



Chart China Beats U S Europe In Combined Greenhouse Gases Statista
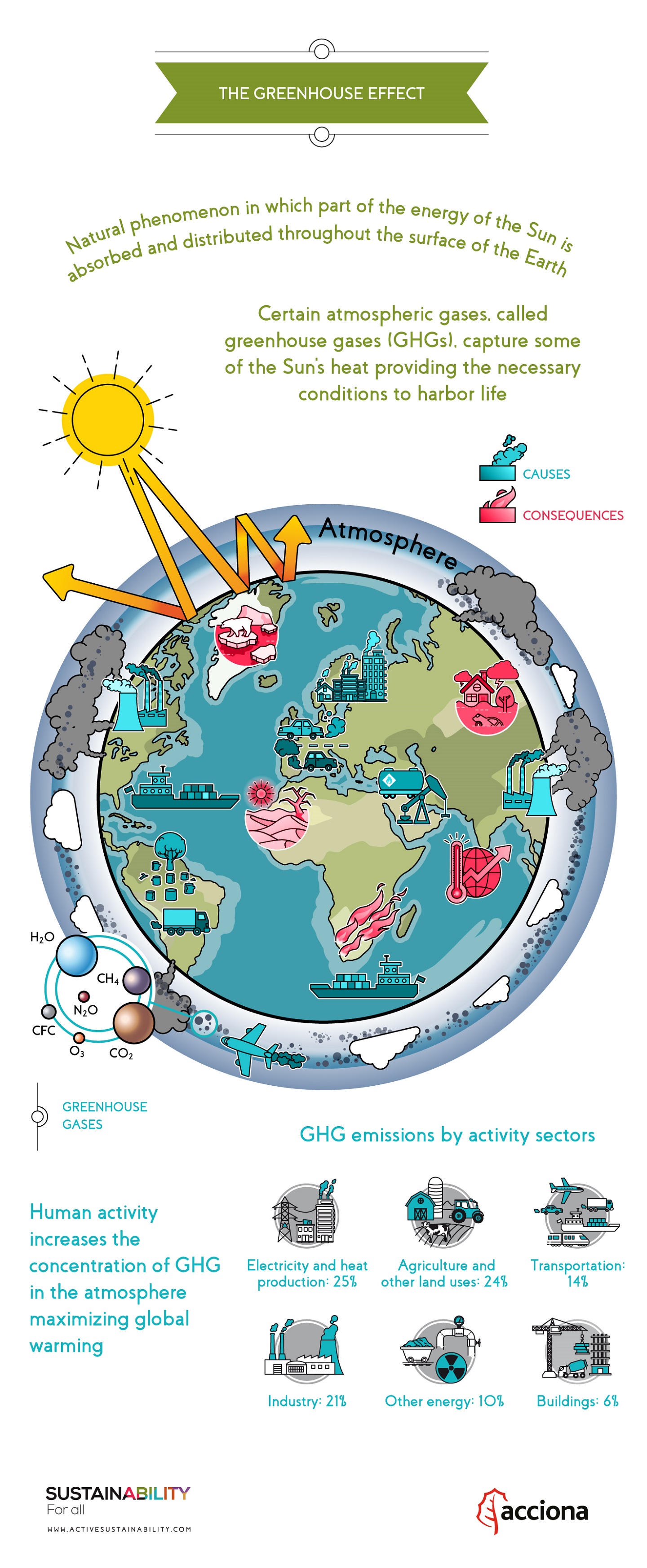



What Is The Greenhouse Effect




If Emissions Of Greenhouse Gases Were Stopped Would The Climate Return To The Conditions Of 0 Years Ago Royal Society




Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿